Publications
2024
-
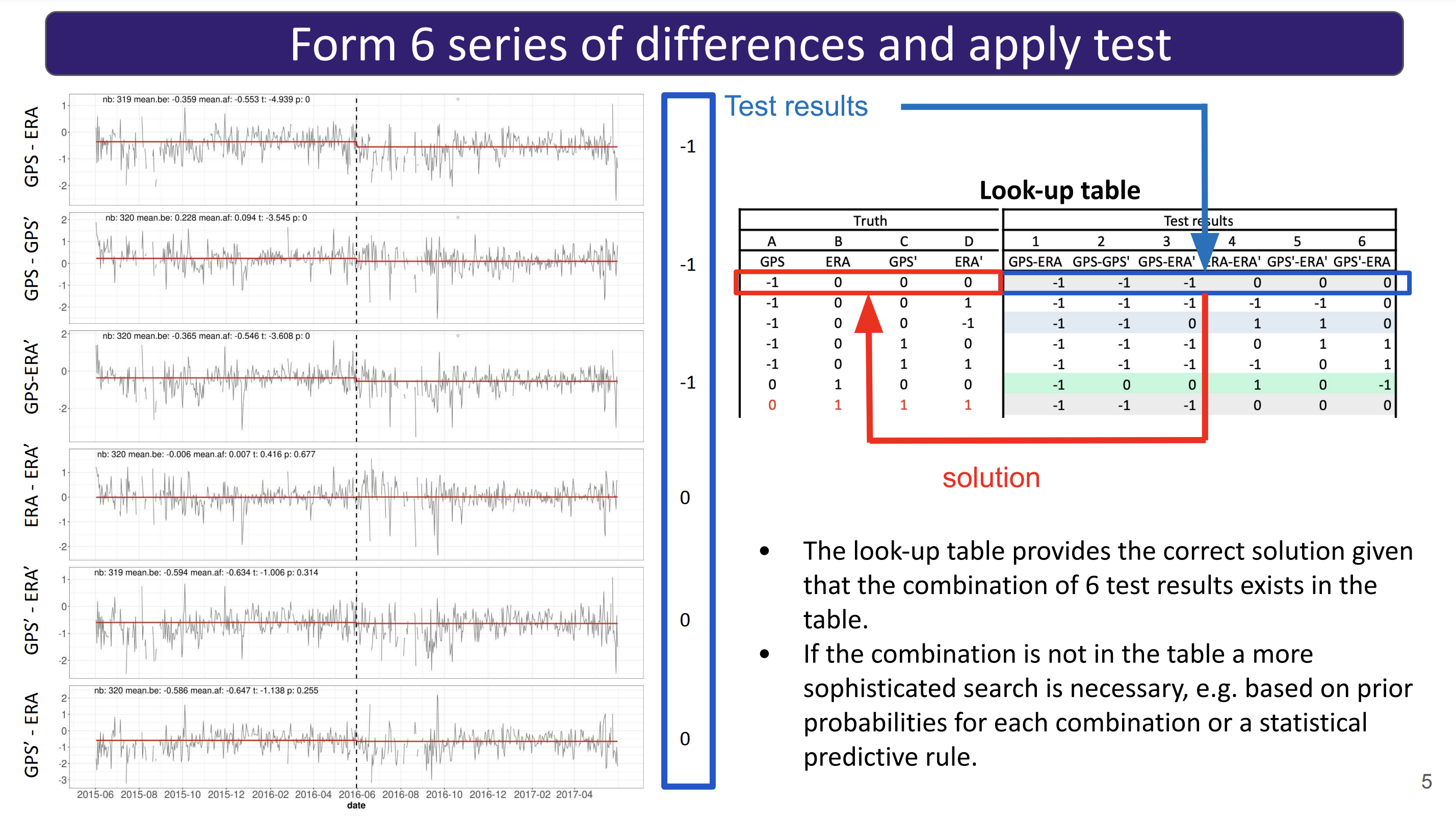 A statistical method for the attribution of change-points in segmented Integrated Water Vapor difference time seriesNguyen, Khanh Ninh, Bock, Olivier, and Lebarbier, EmilieInternational Journal of Climatology 2024
A statistical method for the attribution of change-points in segmented Integrated Water Vapor difference time seriesNguyen, Khanh Ninh, Bock, Olivier, and Lebarbier, EmilieInternational Journal of Climatology 2024Abstract Many segmentation or change-point detection methods for homogenizing climate time series compare candidate station data with reference data to eliminate common climate signals and more efficiently detect spurious, non-climatic changes. One drawback is that it is difficult to decide whether the detected change-point is due to the candidate series or to the reference. A so-called attribution procedure is typically applied in a post-processing step for each detected change-point. This article describes a new statistical method for the attribution of change-points detected in Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) minus reanalysis series of integrated water vapour. It requires at least one nearby station with similar GNSS and reanalysis data. Six series of differences are formed from the four base series (BS) and are tested for a significant jump at the time of the change-point detected in the candidate station. The six test results are analysed with a statistical predictive rule to attribute the change-point to one, or several, of the four BS. Original aspects of our method are: (1) the significance test, which is based on a generalized linear regression approach, taking both heteroscedasticity and autocorrelation into account; (2) the predictive rule, which uses a machine learning method and is constructed from the test results obtained with the real data by using a resampling strategy. Four popular machine learning methods have been compared using cross-validation and the best one was applied to a real data set (49 main stations with 114 change-points). The results depend on the choice of the test significance level and the aggregation method combining the prediction results when several nearby stations are available. We find that 62% of the change-points are attributed to GNSS, 19% to the reanalysis, and 10% are due to coincident detections.
@article{nguyen2024, author = {Nguyen, Khanh Ninh and Bock, Olivier and Lebarbier, Emilie}, title = {A statistical method for the attribution of change-points in segmented Integrated Water Vapor difference time series}, journal = {International Journal of Climatology}, year = {2024}, keywords = {change-point detection, generalized least squares, GNSS, homogenization, reanalysis, segmentation, supervised classification}, doi = {10.1002/joc.8441}, url = {https://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/joc.8441}, }
2021
-
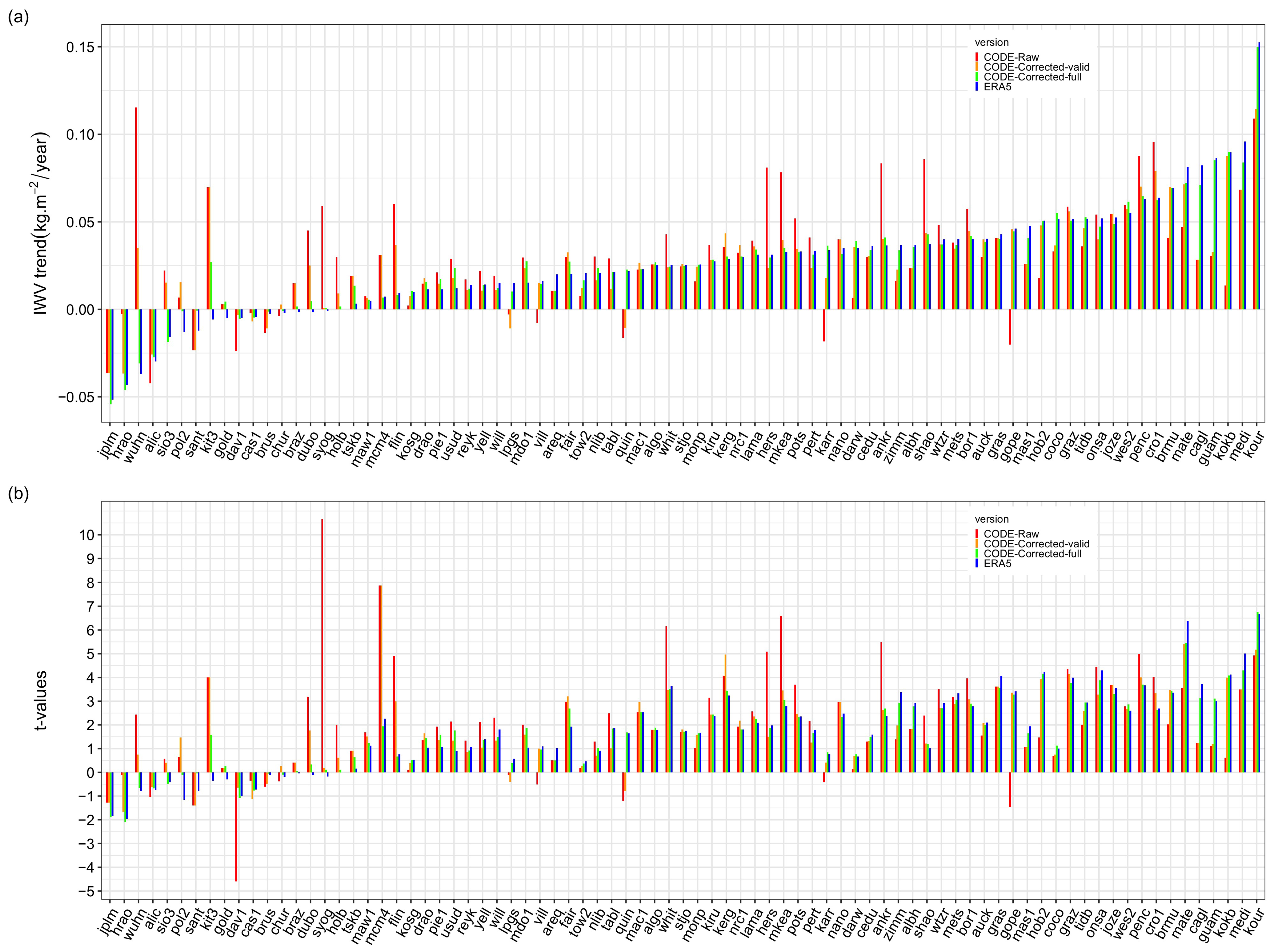 Sensitivity of Change-Point Detection and Trend Estimates to GNSS IWV Time Series PropertiesNguyen, Khanh Ninh, Quarello, Annarosa, Bock, Olivier, and Lebarbier, EmilieAtmosphere 2021
Sensitivity of Change-Point Detection and Trend Estimates to GNSS IWV Time Series PropertiesNguyen, Khanh Ninh, Quarello, Annarosa, Bock, Olivier, and Lebarbier, EmilieAtmosphere 2021This study investigates the sensitivity of the GNSSseg segmentation method to change in: GNSS data processing method, length of time series (17 to 25 years), auxiliary data used in the integrated water vapor (IWV) conversion, and reference time series used in the segmentation (ERA-Interim versus ERA5). Two GNSS data sets (IGS repro1 and CODE REPRO2015), representative of the first and second IGS reprocessing, were compared. Significant differences were found in the number and positions of detected change-points due to different a priori ZHD models, antenna/radome calibrations, and mapping functions. The more recent models used in the CODE solution have reduced noise and allow the segmentation to detect smaller offsets. Similarly, the more recent reanalysis ERA5 has reduced representativeness errors, improved quality compared to ERA-Interim, and achieves higher sensitivity of the segmentation. Only 45–50% of the detected change-points are similar between the two GNSS data sets or between the two reanalyses, compared to 70–80% when the length of the time series or the auxiliary data are changed. About 35% of the change-points are validated with respect to metadata. The uncertainty in the homogenized trends is estimated to be around 0.01–0.02 kg m−2 year−1.
@article{atmos12091102, author = {Nguyen, Khanh Ninh and Quarello, Annarosa and Bock, Olivier and Lebarbier, Emilie}, title = {Sensitivity of Change-Point Detection and Trend Estimates to GNSS IWV Time Series Properties}, journal = {Atmosphere}, volume = {12}, year = {2021}, number = {9}, article-number = {1102}, url = {https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/12/9/1102}, issn = {2073-4433}, doi = {10.3390/atmos12091102}, }